Note
Click here to download the full example code
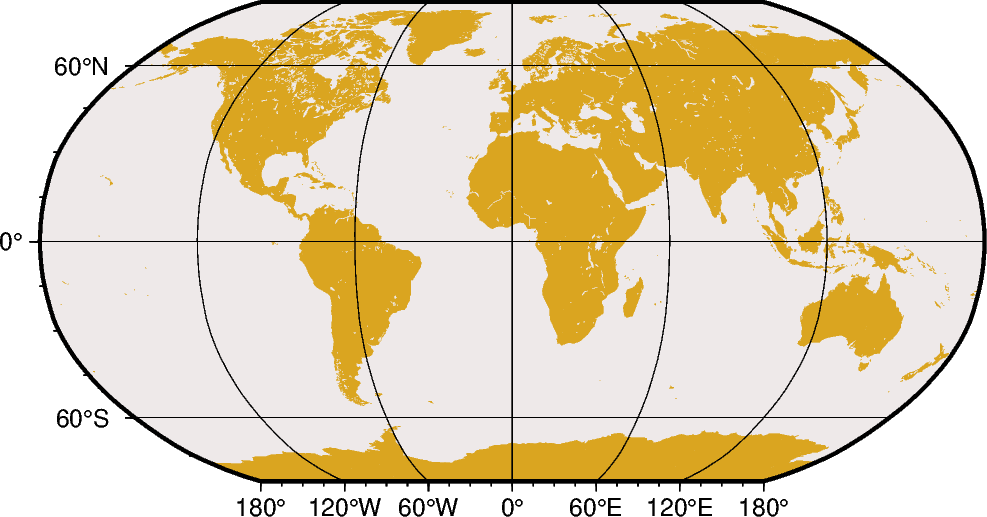
Robinson¶
The Robinson projection, presented by the American geographer and cartographer Arthur H. Robinson in 1963, is a modified cylindrical projection that is neither conformal nor equal-area. Central meridian and all parallels are straight lines; other meridians are curved. It uses lookup tables rather than analytic expressions to make the world map “look” right 22. The scale is true along latitudes 38. The projection was originally developed for use by Rand McNally and is currently used by the National Geographic Society.
n[lon0/]scale or N[lon0/]width
The projection is set with n or N. The central meridian is set with the optional lon0, and the figure size is set with scale or width.
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
import pygmt
fig = pygmt.Figure()
# Use region "d" to specify global region (-180/180/-90/90)
fig.coast(region="d", projection="N12c", land="goldenrod", water="snow2", frame="afg")
fig.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.960 seconds)